Written by: Wang Xue
Translated by: Li Xiaojuan
Recently, Professor He Qiang from Key Laboratory of Microsystems and Microstructures Manufacturing, Ministry of Education, Harbin Institute of Technology with his team has successfully developed the world's first artificial two-engine mode micro/nanosized machines. These machines are with potentials to be applied in biomedicine, environment screening as well as micro/nano assembly and fabrication
The research findings are published in Journal of the American Chemical Society, a renowned international journal. The article is titled Bubble-Pair Propelled Colloidal Kayaker, and its first author is Doctor Wu Yingjie, associate professor of School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering. In addition, this article appears on the cover of the Journal in its issue.
Chemically powered micro/nanosized machine is a micro/nanosized system that converts chemical energy into self-propelled movement. It’s now a popular interdisciplinary science that covers material science, robot engineering, physics, chemistry, and biomedicine etc. The research team led by Professor He Qiang has pioneeringly introduced controlled chemical assembly approach to prepare single bubble propelled anode/cathode capsule motor and tubular nanomotors (i.e. nano-rocket). However, it remains to be a challenge to mimic the widely existing two-engine mode motion in nature (such as the motion of a swimming penguin), by which the artificial two-engine mode micro/nanosized machine can be applicable to complex environments in the future.
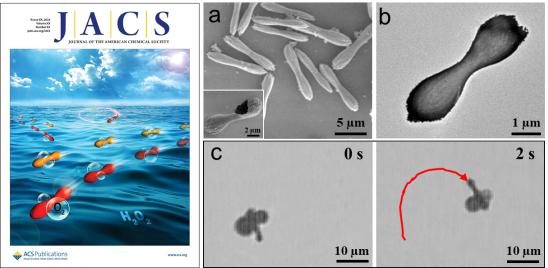
The research team synthesized hollow dumbbell-shaped manganese dioxide (MnO2) by hydrothermal synthesis method. The hollow MnO2 can catalytically decompose hydrogen peroxide fuel to oxygen. Because of its dumbbell-shaped geometry, two breathing oxygen bubbles generated on the waist of the particle which either grows synchronously or asynchronously to propel the motor to move in fluid at low Reynold number condition. Because this mode of motion is similar to a single kayak with a double-bladed paddle, the hollow dumbbell-shaped MnO2 is called "colloidal kayak" vividly.
Due to the unique dumbbell shape of the hollow MnO2, the reaction force caused by the growth and release process of the bubble pair has nonzero projections both to the tangential axis (long axis) and radial axis, which contribute the driving force and torque on the colloidal kayaker, respectively. The driving force pushes the colloidal kayaker to move forward, whereas the torque turns its direction as it moves. In addition, this research has analyzed the statistics of synchronous or asynchronous growth process of bubble pair, and it has also simulated the changes in fluid field around bubbles during their growth and release process. in this way, this research formulated a physical model of bubble growth dynamics and equation of particle motion, which can better explain its motion mechanism.
The research shows that bubble pair propulsion is more flexible than single bubble mode. This finding is with far-reaching significance for exploring the design method of two-engine mode micro/nanosized machines and developing researches for applications adapted to complex environment.